
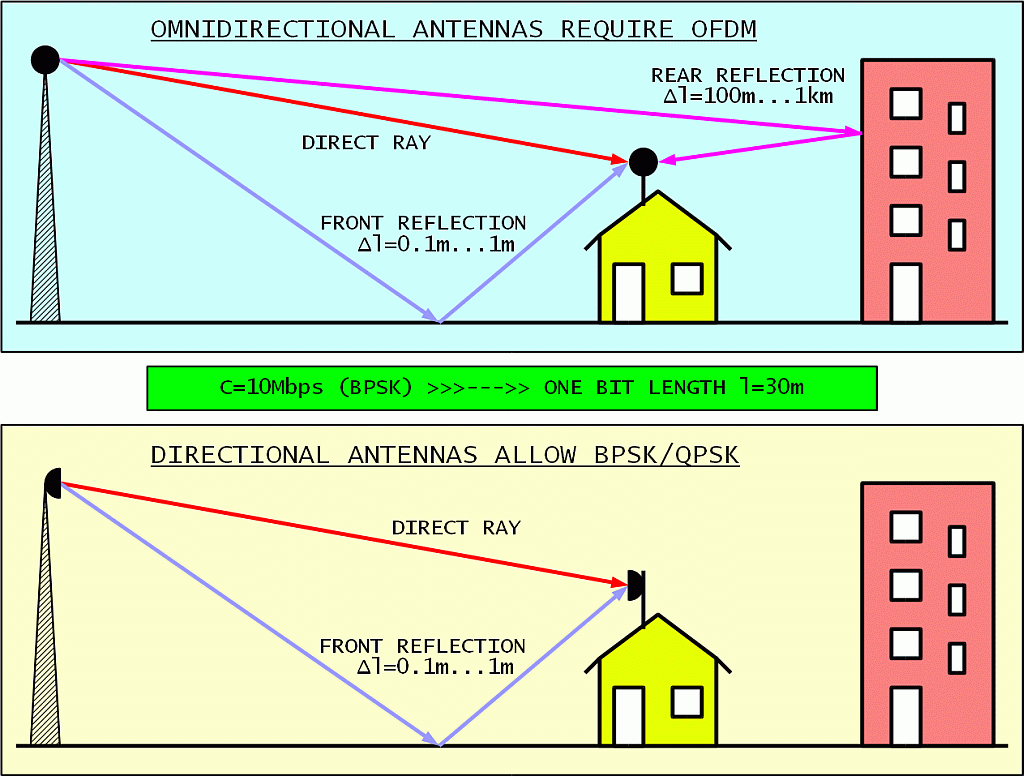

The move will let Microsoft customers run SAP software without installing it on their own servers. SAP’s Hana data analysis tools and S/4 Hana applications will be able to run on Microsoft’s Azure cloud computing service by the third quarter of 2016, the companies announced Tuesday. and SAP SE are linking up their software products to make it easier for businesses to rent applications online and workers to manage travel and meetings. See also velocity factor and radio propagation.Microsoft Corp. For example, in the case of an electric signal, it is the time taken for the signal to travel through a wire. In physics, particularly in the electromagnetic field, the propagation delay is the length of time it takes for a signal to travel to its destination. Logic gates can have propagation delays ranging from more than 10 ns down to the picosecond range, depending on the technology being used. Wires have an approximate propagation delay of 1 ns for every 6 inches (15 cm) of length. If the output of a logic gate is connected to a long trace or used to drive many other gates (high fanout) the propagation delay increases substantially. All of these factors influence each other through an RC time constant: any increase in load capacitance increases C, heat-induced resistance the R factor, and supply threshold voltage increases will affect whether more than one time constants are required to reach the threshold.
Increases in output load capacitance, often from placing increased fan-out loads on a wire, will also increase propagation delay. Marginal increases in supply voltage can increase propagation delay since the upper switching threshold voltage, V IH (often expressed as a percentage of the high-voltage supply rail), naturally increases proportionately. Propagation delay increases with operating temperature, as resistance of conductive materials tends to increase with temperature. The principle of logical effort utilizes propagation delays to compare designs implementing the same logical statement. The difference in propagation delays of logic elements is the major contributor to glitches in asynchronous circuits as a result of race conditions. The determination of the propagation delay of a combined circuit requires identifying the longest path of propagation delays from input to output and by adding each propagation delay along this path. Reducing gate delays in digital circuits allows them to process data at a faster rate and improve overall performance. This may depend on the direction of the level change, in which case separate fall and rise delays t PHL and t PLH or t f and t r are given. Often on manufacturers' datasheets this refers to the time required for the output to reach 50% of its final output level from when the input changes to 50% of its final input level. In electronics, digital circuits and digital electronics, the propagation delay, or gate delay, is the length of time which starts when the input to a logic gate becomes stable and valid to change, to the time that the output of that logic gate is stable and valid to change.

#Longest signal path four bit or full#
A full adder has an overall gate delay of 3 logic gates from the inputs A and B to the carry output C out shown in red


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
